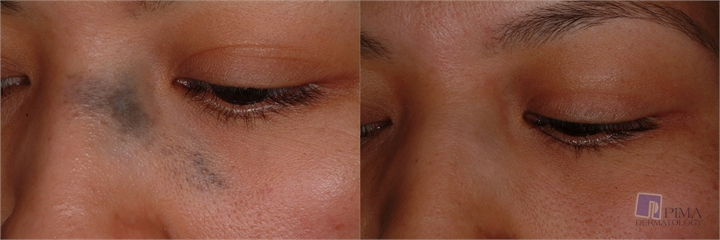
Nevus of Ota presents as a blue or gray patch on the face. It is caused by the entrapment of melanocytes in the upper third of the dermis. The nevus can either be unilateral or bilateral and, in addition to skin, it may also involve the ocular and oral mucosal (the first two branches of the trigeminal nerve; the temple region, eyebrow region or below the eyes and often extending to the ear or the nose etcetera). The sclera is involved in two-thirds of cases (causing an increased risk of glaucoma). Women are nearly five times more likely to be affected than men. Nevus of Ota often appears during puberty.
Nevus of Ota presents as a blue or gray patch on the face. It is caused by the entrapment of melanocytes in the upper third of the dermis. The nevus can either be unilateral or bilateral and, in addition to skin, it may also involve the ocular and oral mucosal (the first two branches of the trigeminal nerve; the temple region, eyebrow region or below the eyes and often extending to the ear or the nose etcetera). The sclera is involved in two-thirds of cases (causing an increased risk of glaucoma). Women are nearly five times more likely to be affected than men. Nevus of Ota often appears during puberty.
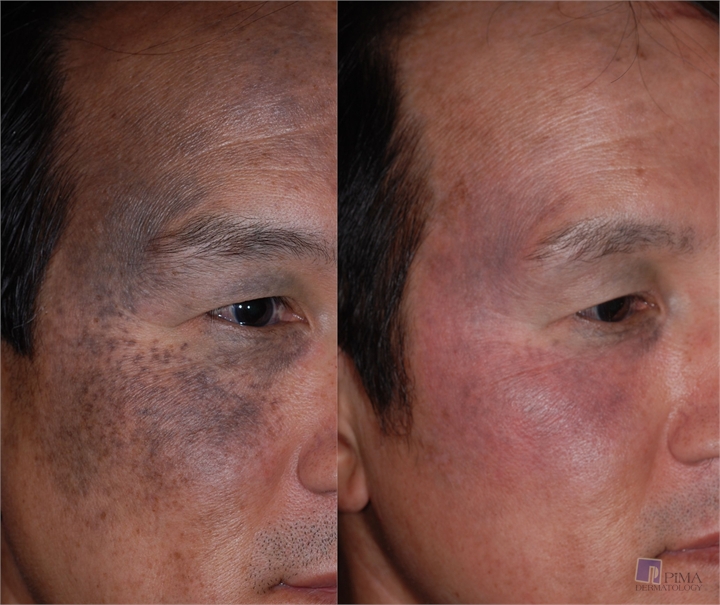
Before and After
Next, read about poikiloderm (red neck).